|
Multi-niche crowding method (MNC)
modifies the selection system as well as
the substitution one. This method
introduces a selective pressure by
having tournaments among groups of
individuals to select the parents.
Instead of using the parents in the
replacement, various groups of solutions
of the initial population are used. The
individuals with the most similarities
to the child in each group will be
selected, and from these, the individual
with the worst quality will be
substituted.
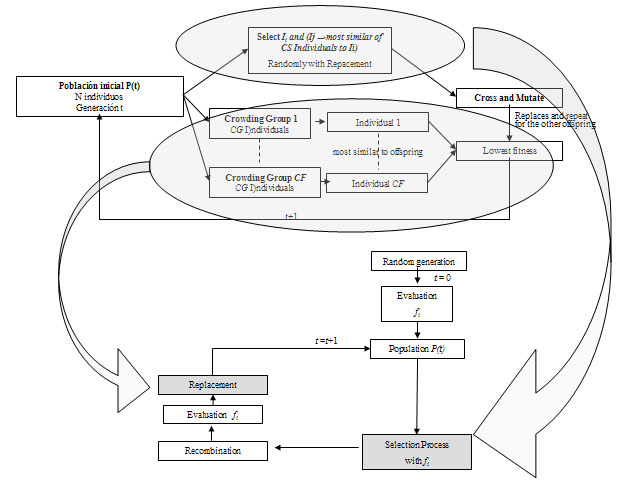
In the MNC method the following
process of selection takes place: an
individual is selected randomly (Ii)
and its pair (Ij) will
be the closest to the CS
individuals (crowding selection group
size) selected randomly from the
population with replacement. Thus, the
recombination happens among individuals
of the same niche, but not totally
restricting the possibility to explore
among niches.
During
the replacement the policy followed is
the worst among most similar.
Hence,
from the initial population,
CF
groups are made of
CG
size with random replacements. From each
group the individual with the most
similarities to the child which has just
been obtained is achieved, and from
these individuals the worst is selected
and replaced by the child.
This process is
shown in the following flowchart:
This method cannot be
considered of type steady state as each
child introduced in the population after
the substitution is not available for
the selection, but only for the
substitution. I.e., from the initial
population we obtain N parents
necessary for reproduction (with only
one step) by means of tournament. Once
this is performed, each individual of
the children population goes through the
substitution process. The first child
substitutes an individual from the
initial population. For the second child
the process is repeated but counting on
the first child that is already inside
the population from which the groups for
substitution are formed.. So for child
j prior children j-1 will
be in the population.
|

